AI is transforming project management by using data to predict outcomes like budgets, timelines, and risks with greater accuracy than older methods. Here's what you need to know:
- Why It Matters: AI can forecast delays or budget overruns weeks in advance, helping managers make adjustments early. Deep learning models, for instance, achieve 85–90% accuracy in cost predictions, compared to 70–80% with traditional methods.
- How It Works: AI analyzes historical and real-time data to identify patterns. Algorithms like Random Forests, Gradient Boosting Machines, and Neural Networks excel at handling complex variables like team dynamics or market changes.
- Key Algorithms:
- Random Forests: Reduce errors by averaging predictions from multiple decision trees.
- XGBoost: Handles outliers and missing data, achieving up to 92% accuracy in some cases.
- Neural Networks: Model non-linear relationships, like how adding team members mid-project could slow progress.
- Data Inputs: Clean, standardized historical metrics (e.g., budgets, timelines) and real-time data (e.g., IoT sensors, market prices) are essential for reliable AI predictions.
- Challenges: Poor data quality, algorithm bias, and employee resistance to AI adoption can hinder success. Organizations need to address these issues by improving data standards and training teams.
AI-driven predictions are helping companies deliver more projects on time and within budget. While challenges remain, the benefits of better forecasting and risk management are reshaping project management.
Can AI Really Predict Project Outcomes? Conversation with Lloyd Skinner of Greyfly.ai
AI Algorithms Used for Project Predictions
Accurate project forecasts hinge on algorithms that can identify patterns within historical data. These tools, ranging from decision-tree models to neural networks, are designed to emulate how the human brain processes information. By understanding the algorithms behind predictive analytics, project managers can make smarter choices about which tools best suit their needs. Let’s explore some of the key algorithms driving these predictions.
Random Forests, GBMs, and Neural Networks
Random Forests operate by generating multiple decision trees, each analyzing different data subsets, and then averaging their predictions to minimize errors. This method works particularly well for tasks like classifying risks or forecasting resource needs and cost changes. For example, a case study showed that combining Random Forests with Support Vector Machines led to an 18% reduction in project delays and a 25% improvement in resource estimation accuracy.
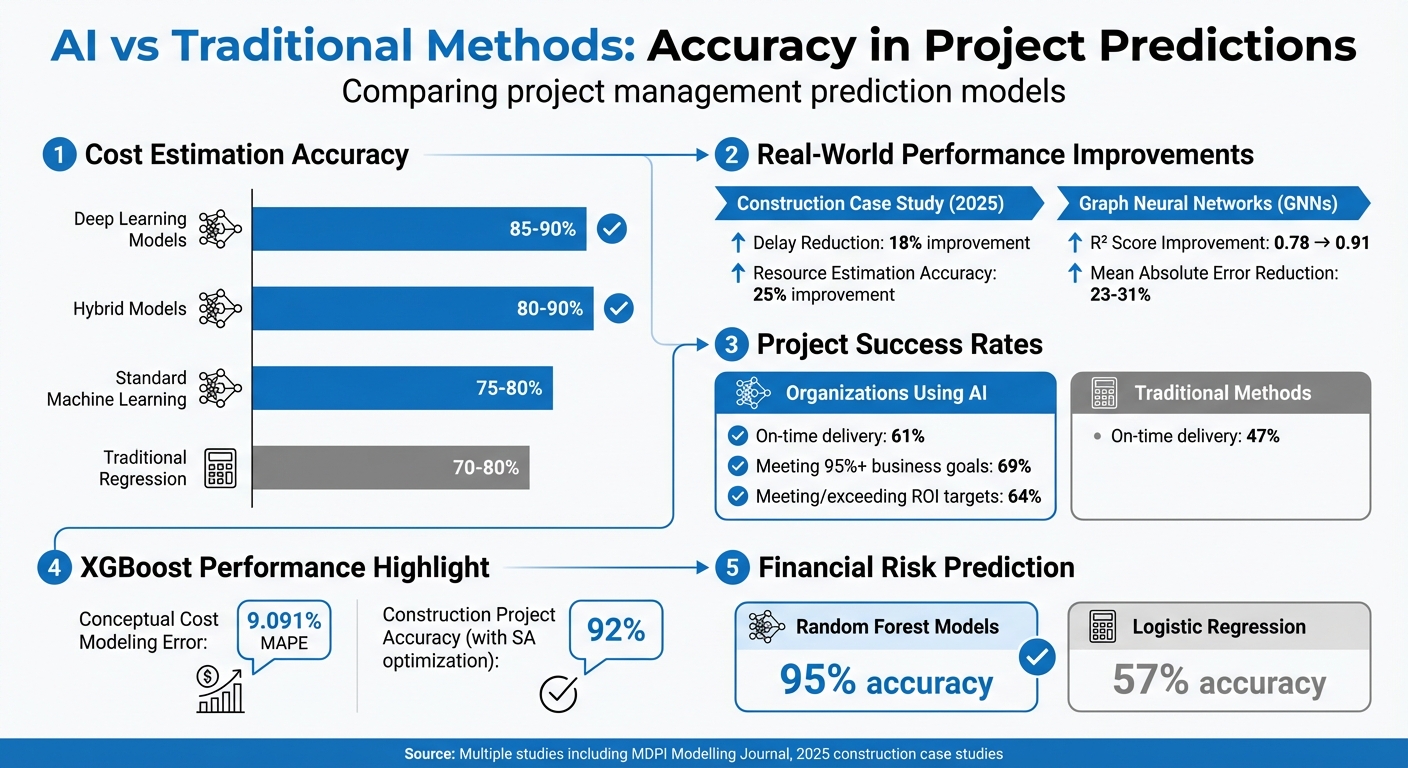
Gradient Boosting Machines (GBM) and XGBoost take a different approach by building models in sequence, where each new model addresses the errors of the previous one. XGBoost is especially effective at handling missing values and outliers - common issues in project datasets - while also being easy to interpret. Studies highlight its strength in conceptual cost modeling, achieving a mean absolute percentage error of just 9.091%. When paired with Simulated Annealing optimization (XGBoost-SA), it delivers 92% prediction accuracy for construction projects.
Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) excel at capturing complex, nonlinear relationships between variables. For instance, they can model how adding team members mid-project might inadvertently slow progress due to increased communication overhead. Variants like RNNs and LSTMs are particularly suited for time-series forecasting, tracking how costs or schedules shift over a project's lifecycle. Additionally, Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have proven to reduce mean absolute error by 23% to 31%, outperforming traditional methods by mapping projects as interconnected networks of tasks and resources.
"AI-powered approaches, particularly artificial neural networks (ANNs)... enhance predictive accuracy and adaptability to complex, dynamic project environments." - MDPI Modelling Journal
The choice of algorithm often depends on the project's complexity and the amount of data available. Neural networks, for instance, can achieve 85–90% accuracy in cost estimation but require large datasets to perform effectively. For smaller projects with limited historical data, Random Forests or XGBoost might strike a better balance between accuracy and feasibility.
Ensemble Methods for Better Accuracy
Individual models are powerful, but combining multiple approaches can take accuracy to the next level. Ensemble methods aggregate predictions from several models, improving reliability. When multiple algorithms converge on the same result, it’s a strong indicator that the prediction is trustworthy.
There are three main ensemble strategies, each offering unique advantages:
- Bagging, used in Random Forests, builds multiple models simultaneously on different data subsets and averages their outputs. This reduces variance and improves stability.
- Boosting, as seen in Gradient Boosting Machines, trains models sequentially, with each one correcting the errors of the last, effectively reducing bias.
- Stacking combines entirely different model types - like pairing a Support Vector Machine with a Neural Network - to capture diverse perspectives from the data.
In financial risk prediction, a critical aspect of project management, Random Forest models achieved a striking 95% accuracy, far surpassing Logistic Regression models, which only managed 57%.
"Ensemble learning - aggregating multiple models - can enhance predictive performance by capturing diverse aspects of the data." - Kamil Samara, Computer Science Department, University of Wisconsin–Parkside
Another advantage of ensemble methods is their ability to rank the importance of different features. For example, they can identify which factors - such as labor costs, material price fluctuations, or weather conditions - have the greatest impact on project outcomes. This level of transparency not only clarifies what the model predicts but also why, empowering project managers to allocate resources and attention more effectively.
Data Inputs Required for Accurate Predictions
Historical Metrics and Real-Time Data
Once you've delved into AI algorithms, the next step is understanding the data inputs that power them. Without the right data, even the most advanced models won't deliver reliable predictions.
AI models thrive on diverse inputs. Historical project data - especially from similar scopes - helps algorithms identify recurring patterns. For instance, temporal data comparing planned versus actual timelines is crucial for spotting delays. Seasonal trends, like slower construction progress during winter or holiday-related software release delays, also provide valuable context.
Financial inputs play a major role, too. Historical budgets, material price fluctuations, and inflation rates all shape forecast accuracy. Different contract types - like fixed-price versus cost-plus - add another layer of complexity, as they create varying risk profiles that AI systems can learn to navigate. External market forces, such as unexpected spikes in material costs, also influence project expenses and need to be factored in.
Resource allocation data is equally critical. Details about how team members, equipment, and materials were distributed in past projects feed into AI models, enabling better predictions. For example, in construction, analyzing pre-measurement data from blueprints helps establish baseline cost estimates.
Modern systems take it a step further by incorporating real-time data. IoT sensors, up-to-date commodity prices, and automated schedule updates refine predictions on the fly. Some advanced implementations even analyze social media sentiment to anticipate regulatory hurdles or public opposition that could cause delays.
Data Quality Standards
High-quality predictions depend on high-quality data. If the input data is messy, incomplete, or inconsistent, the forecasts will be unreliable. To ensure accuracy, three core standards are essential: clean data (free from errors), complete data (no missing milestones or metrics), and consistent data (uniformly recorded across the organization).
Standardization in data collection is just as important. When teams define metrics differently - like marking "project completion" at client sign-off versus final payment - it creates inconsistencies that can obscure critical patterns. Conducting a data readiness audit before deploying AI tools can help identify and fix these issues.
Data normalization is another key step. It ensures variables measured on different scales can be compared. For example, comparing a $50,000 website redesign to a $5 million infrastructure project requires adjusting for scale. Similarly, categorical data (like "low", "medium", or "high" risk ratings) must be converted into numerical values, using techniques like RIDIT scoring, to make them usable by algorithms.
To further improve predictions, advanced AI systems use feature extraction to filter out irrelevant data. This reduces "noise" and focuses on the most meaningful variables. Research shows that approximately 70% of recent studies in cost estimation now rely on machine learning and deep learning techniques for this very reason. Some algorithms can analyze up to 44 independent variables at once - from labor metrics to contractual issues - to forecast outcomes. Feature weighting, where more importance is assigned to historically impactful variables, can further enhance model accuracy.
Accuracy Rates and Performance Benchmarks
AI vs Traditional Methods: Project Management Accuracy Comparison
Accuracy in Predicting Delays and Budget Overruns
AI-powered models have proven to be more effective than traditional methods by tapping into nonlinear relationships and utilizing real-time data insights.
Take cost estimation, for example: deep learning models typically achieve accuracy rates of 85–90%, hybrid models range between 80–90%, standard machine learning approaches fall between 75–80%, and traditional regression methods hover around 70–80%.
In a 2025 construction case study, integrating machine learning reduced delays by 18% and boosted resource estimation accuracy by 25% when compared to manual methods. Graph Neural Networks (GNNs), known for their ability to model task-resource dependencies, enhanced the coefficient of determination (R²) from 0.78 to 0.91 in large-scale, intricate project networks. This leap translates to a 23% to 31% drop in mean absolute error for time and cost predictions versus traditional tree-based methods.
These numbers highlight AI's growing role in reshaping project management.
"AI-powered approaches, particularly artificial neural networks (ANNs) - which constitute 26.33% of the studies - enhance predictive accuracy and adaptability to complex, dynamic project environments." - MDPI Modelling
The success of these models emphasizes the importance of selecting the right AI approach and ensuring access to high-quality data, a topic we’ll delve into next.
Factors That Affect Prediction Performance
While these performance benchmarks are impressive, several variables can influence the accuracy of AI predictions. Robust historical data is critical for models to adapt effectively to market trends.
The type of algorithm used also matters. Deep learning and hybrid models excel in handling complex, nonlinear projects like large infrastructure developments. On the other hand, simpler regression models are better suited for projects with clear, linear relationships. Misaligning the model with the project type can significantly impact both accuracy and efficiency.
External factors add another layer of complexity. Variables like contract pricing structures, regional cost overruns, and even weather conditions can affect model performance. For instance, an analysis of 276 engineering projects revealed an average cost overrun of 12.22%, with infrastructure projects in Asia facing even higher rates of 26.24%. Another study focusing on 122 Qatari construction contracts found that 72% of them experienced deadline extensions. For AI models to provide reliable predictions, they need to account for these regional and contractual variations.
sbb-itb-bec6a7e
How Predictive Analytics Is Used in Project Management
With the help of advanced algorithms and high-quality data, predictive analytics has become a game-changer in proactive project management.
Risk Mitigation and Resource Optimization
Predictive analytics identifies risks by diving deep into complex project data. AI tools analyze factors like fluctuating material costs, labor availability, and regional wage differences to help managers address risks ahead of time.
What sets this technology apart is its ability to zero in on specific high-risk factors rather than issuing broad, generic alerts. For example, AI can identify the root causes of cost and schedule overruns, enabling managers to focus on the most pressing challenges. It also facilitates scenario-based planning, allowing teams to evaluate potential outcomes before committing resources.
Incentive-driven strategies, such as performance bonuses in cost-plus contracts, can help control overruns. However, in fixed-price contracts, these same strategies might inadvertently lead to additional expenses.
"Machine learning algorithms efficiently handle multi-dimensional and multi-variety data in dynamic or uncertain environments."
- Shahadat Uddin, Stephen Ong, and Haohui Lu
Beyond identifying risks, AI enhances budgeting and scheduling, improving overall project performance.
Budget Management and Task Duration Forecasting
AI's predictive powers go beyond risk management, offering sharper cost and timeline forecasts. By uncovering complex, non-linear relationships between cost-driving factors - like market trends, inflation, and material price shifts - AI provides insights that traditional methods often miss.
AI models continuously adapt project timelines by analyzing resource usage, task dependencies, and evolving constraints. This dynamic approach replaces static schedules, which can quickly become outdated after a project begins.
Automated task prioritization further streamlines scheduling and enhances efficiency. Predictive analytics doesn’t just react to problems - it anticipates them, allowing for proactive adjustments that safeguard project outcomes.
"The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Big Data Analytics (BDA) in project management has become a critical enabler of efficiency in managing large-scale, complex projects."
- Muhammad Zahaib Nabeel, PMO Manager, United Technology Holding
Challenges in Using AI Predictions
Using AI for predictive tools in project management comes with its own set of challenges.
Algorithm Bias and Transparency Issues
AI predictions heavily depend on the quality of the data they are trained on. If the historical data contains inefficiencies or biases, these flaws can carry over into the AI's predictions. For example, if the training data includes records from a time when delays were frequent, the AI might wrongly assume such delays are unavoidable instead of recognizing them as preventable risks.
Another issue is proxy data bias. When AI systems use indirect indicators, like postal codes as a stand-in for economic status, they risk introducing unintended demographic biases into decision-making processes. This can lead to unfair resource allocation and systematically biased predictions that negatively impact certain groups.
"If we can build a model that identifies offenders correctly 80 out of 100 times, what happens to the poor souls in the 20 percent? Our model is going to harass them over and over and over again." - Charles Wheelan, Author of "Naked Statistics"
Additionally, the "black box" nature of AI models - where the decision-making process is opaque - can erode trust. To counter this, organizations can implement measures like human-in-the-loop systems, where experts review AI-driven recommendations before final decisions are made. Regular algorithm audits and the adoption of explainable AI systems that clearly document their processes can also enhance transparency. Building diverse teams to develop these systems is another way to uncover biases that might otherwise go unnoticed in less varied groups.
Data Gaps and Technology Adoption Barriers
Beyond bias, the quality and availability of data, along with technology readiness, pose significant challenges. Poor-quality data leads to unreliable predictions, making it harder for AI to identify patterns that could predict cost overruns or delays. Gaps in data - whether due to missing, unstructured, or inaccessible information - further limit the effectiveness of advanced analytics. With only 35% of projects globally deemed successful and an estimated $48 trillion invested in projects annually, these data issues have enormous financial consequences.
High upfront costs and outdated digital infrastructure also make it difficult for many organizations to collect and manage quality data. On top of this, employees often resist AI adoption due to fears of job displacement.
To address these challenges, organizations can take steps such as converting continuous data into categories (e.g., labeling costs as "low" or "high"), standardizing text into numerical data, and using techniques like k-fold cross-validation to improve model performance with limited datasets. Upskilling employees to interpret AI outputs and spot algorithmic biases can further reduce resistance and help build trust in these systems.
Emerging regulations add another layer of complexity. For instance, under the EU AI Act, violations could result in fines of up to EUR 35 million or 7% of global annual turnover. Tackling these challenges is essential to fully harnessing AI's potential in project management.
Conclusion
Key Takeaways
AI-driven predictions are changing the game for project management. Organizations leveraging these tools see a notable boost in performance - 61% of projects are delivered on time compared to 47% with traditional methods. Additionally, 69% of these organizations hit 95% or more of their business goals, with 64% meeting or exceeding their original ROI targets. When it comes to cost estimation, deep learning models achieve an impressive 85–90% accuracy, while hybrid models reach 80–90% for more complex projects. This level of precision empowers project managers to pinpoint the main factors behind cost and schedule overruns, allowing them to act before minor issues become major setbacks.
"A carefully curated machine learning approach can help achieve superior prediction metrics" - Xiaochen Kev Gao, Rady School of Management, UCSD
For small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), the move from reactive reporting to proactive analytics means fewer unpleasant surprises and smarter use of resources. AI not only predicts potential challenges but also suggests actionable solutions. The foundation for success lies in clean, standardized historical data and selecting models that align with your project's complexity. However, AI isn't foolproof - human oversight is essential to address biases and inaccuracies. By following these steps, organizations can make informed decisions when choosing tools, ensuring they maximize the value of their investment.
Finding the Right AI Tools
With the proven advantages of AI in mind, the next step is choosing the right tool for your needs. For SMEs, platforms with AutoML capabilities are a great starting point, as they enable teams without advanced data science skills to create reliable predictive models. It's also important to look for tools that seamlessly integrate with your existing CRM or ERP systems, offer customizable dashboards, and are easy to learn.
Platforms like AI for Businesses simplify this process by helping SMEs find curated AI tools tailored to their operations. Whether you're looking for solutions in project scheduling, resource planning, or budget forecasting, directories like this can save time and help you avoid tools that don’t fit your workflow. Start with a small pilot project, test the waters, and gradually scale as your team becomes more comfortable with AI-driven insights. This measured approach can transform how your organization manages projects, delivering better outcomes and greater efficiency.
FAQs
How does AI address data quality issues when predicting project outcomes?
AI addresses data quality challenges in project predictions by employing sophisticated methods to detect and fix issues like duplicates, inconsistencies, and missing data. Through processes such as data cleaning, validation, and feature selection, AI ensures that the inputs used are reliable, leading to more accurate predictions.
Moreover, today’s AI algorithms are built to handle imperfect data by filtering out irrelevant noise and adjusting to variations. This adaptability enables AI systems to produce precise project forecasts even when dealing with incomplete or flawed information, making them invaluable for project management and informed decision-making.
How can organizations address resistance to adopting AI?
To ease resistance to AI adoption, businesses can take a few practical steps. Start by offering education on how AI actually works - covering its algorithms, capabilities, and overall potential. This helps demystify the technology and reduces fear rooted in uncertainty.
Next, highlight clear benefits through pilot programs or case studies. Show how AI can improve decision-making, streamline processes, and deliver better outcomes. When employees see tangible advantages, they’re more likely to view AI as a helpful tool rather than a disruption.
Lastly, bring stakeholders into the loop early. By involving them in the development and rollout stages, you encourage collaboration and give them a sense of ownership in the process. This approach can make the shift to AI feel less daunting and more inclusive.
How do ensemble methods enhance AI's ability to predict project outcomes?
Ensemble methods significantly boost the predictive accuracy of AI in project management by blending the capabilities of several algorithms, including Random Forest, XGBoost, and LightGBM. This combination helps minimize errors and increases reliability, particularly when working with complex or high-dimensional datasets.
By utilizing a variety of models, ensemble techniques are better equipped to manage uncertainties, delivering more dependable and precise forecasts for project outcomes.


