Proxmox Mail Gateway (PMG) is an open-source email security tool designed to protect your email servers from spam, viruses, and phishing. It works as a mail proxy, sitting between your firewall and mail server, analyzing emails before they reach your infrastructure. Built on Debian, PMG uses trusted tools like Postfix, ClamAV, and SpamAssassin for filtering and security.
Key Highlights:
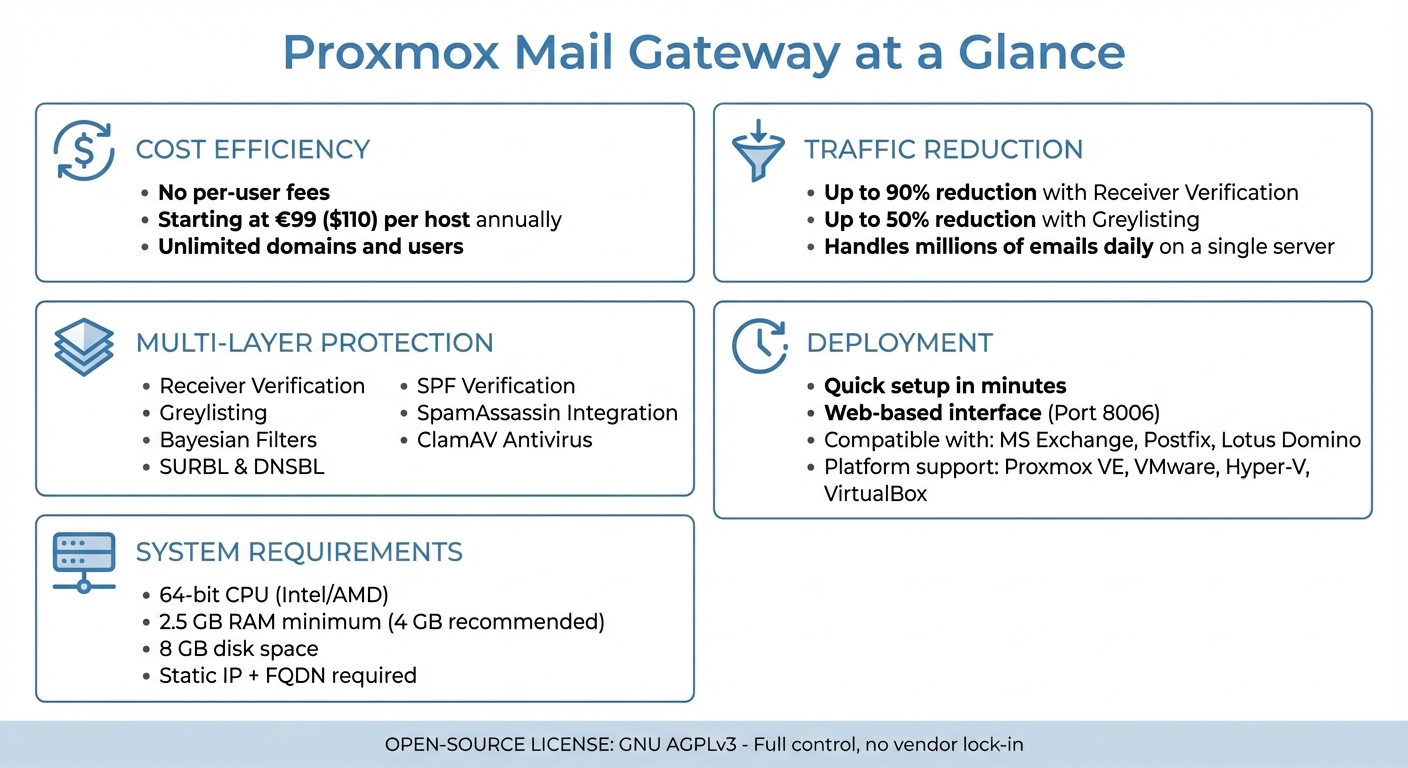
- Cost-Effective: No per-user fees; subscriptions start at $110 per host annually.
- Spam Reduction: Features like Receiver Verification and Greylisting can cut email traffic by up to 90%.
- Outbound Protection: Scans outgoing emails to prevent blacklisting and maintain IP reputation.
- Customizable Rules: Flexible rule system to filter emails based on sender, recipient, content, and more.
- User-Friendly Interface: Web-based management with real-time monitoring, message tracking, and role-based access controls.
PMG supports various email platforms, including Postfix, MS Exchange, and Lotus Domino. It’s easy to install, integrates seamlessly with your email systems, and ensures secure, efficient email management.
Proxmox Mail Gateway Key Features and Benefits Overview
Core Features of Proxmox Mail Gateway
Spam Filtering Capabilities
Proxmox Mail Gateway employs a multi-layered approach to keep spam at bay right at the gateway. One standout feature is Receiver Verification, which checks email recipients at the SMTP level to confirm if the address exists before accepting the message. This method can cut down the volume of emails requiring further spam or virus analysis by up to 90%.
Another effective tool is Greylisting, which temporarily rejects emails from unknown senders. This technique is particularly useful against automated spam campaigns since legitimate mail servers retry delivery within minutes, while infected systems often don’t bother to resend.
The platform also leverages Bayesian Filters, which use statistical algorithms to detect spam patterns. These filters analyze common words and phrases found in spam emails and get better over time as they process more data. As highlighted in the Proxmox Admin Guide:
The system becomes smarter over time... by being trained to recognize those words, the Bayesian filter checks every email and adjusts the probabilities.
These advanced features set the stage for even more robust anti-spam measures.
Additional Anti-Spam Techniques
Proxmox Mail Gateway doesn’t stop at basic filtering - it incorporates advanced detection tools to tackle spam from every angle. Spam URI Real-time Blocklists (SURBL) scan email content for links to spam or phishing sites, while DNS-based Blackhole Lists (DNSBL) check IP addresses against databases of known spam senders. Additionally, Sender Policy Framework (SPF) ensures that the sending mail server is authorized to send on behalf of a specific domain. Integration with SpamAssassin adds another layer of protection, assigning each email a "spam score" based on a variety of tests.
The gateway supports both "Before Queue" and "After Queue" filtering modes. With "Before Queue" filtering, spam is rejected during the SMTP dialogue using a 554 error code, which prevents bounce messages that could lead to blacklisting. On the other hand, "After Queue" filtering accepts the email first and then scans it - ideal when detailed analysis is needed without risking the rejection of legitimate emails during the initial connection.
This combination of detection and filtering ensures comprehensive spam control.
Administration Interface
The Proxmox Mail Gateway’s web-based management interface, accessible on port 8006, provides centralized control over all filtering processes. The Proxmox Message Tracking Center is particularly useful for high-volume environments, summarizing logs to track message arrival, filter results, queue status, and final delivery.
The interface also includes tools for managing quarantined spam, viruses, and blocked attachments. Its Object-Oriented Rule System allows administrators to set up custom filters based on five categories: FROM (sender), TO (recipient), WHEN (timeframe), WHAT (content), and ACTION (what happens to the message). For added security, Role-Based Access Control enables the assignment of roles such as Superuser, Administrator, Quarantine Manager, Auditor, and Helpdesk, ensuring tasks can be delegated securely.
Real-time monitoring tools provide insights into system performance, displaying logs and dashboard visuals for CPU, RAM, disk, and network usage. The Mail Queue Control feature offers a detailed view of pending messages, allowing administrators to inspect email headers and diagnose delivery issues.
Setting Up Proxmox Mail Gateway for Open-Source Email Servers
System Requirements and Installation
To get started with Proxmox Mail Gateway, you'll need a 64-bit CPU (Intel 64 or AMD64), at least 2.5 GiB of RAM (though 4 GiB is better for handling heavy traffic), and 8 GB of disk space. The software is compatible with several virtualization platforms, including Proxmox VE (KVM), VMware vSphere, Hyper-V, VirtualBox, and Citrix Hypervisor. You can install it using the official PMG ISO, which comes with a complete Debian-based operating system. Alternatively, you can deploy it as an LXC container or install it on an existing Debian setup. Make sure to assign a static IP address and a valid Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) .
Once installed, configure your network settings. Open the following ports:
- Port 25: For external SMTP traffic
- Port 26: For internal server communication
- Port 8006: For web management access
- Additional ports: 80, 443, 53, and 123 for updates and related services .
After completing the installation, run the pmgperf command to benchmark your hardware and confirm that everything is functioning as expected. You can then set up custom filtering rules to effectively manage email traffic.
Creating and Managing Rules
Proxmox Mail Gateway uses a flexible rule system to control email flow, organized into five categories: FROM, TO, WHAT, WHEN, and ACTION. Each rule also includes a Direction setting - In, Out, or Both - to specify whether it applies to incoming, outgoing, or all traffic .
- WHO objects: Define senders or recipients, including specific email addresses, domains, regular expressions, IP networks, or LDAP groups.
- WHAT objects: Focus on content characteristics such as spam scores, virus detection, attachment types, or email headers.
- ACTION objects: Specify the outcome, such as Accept, Block, Quarantine, Mark Spam, or Generate Notification .
To streamline operations, add trusted sources to the SMTP Welcomelist. This allows these sources to bypass checks like Greylisting, SPF, and DNSBL, while still applying your filter rules . Rules can be managed through the web GUI, REST API, or the pmgsh command-line tool. For advanced customizations, copy default templates from /var/lib/pmg/templates/ to /etc/pmg/templates/ and modify them there - this ensures your changes persist after updates.
Fine-tuning rules directly improves spam filtering accuracy, making the gateway more effective for your open-source email server.
Deployment Best Practices
For optimal performance, enable outbound scanning. This helps prevent internal virus outbreaks and protects your IP reputation. Configure your internal email server to use Proxmox Mail Gateway as a "smarthost" on port 26 for sending outbound emails .
Another critical step is setting up reverse DNS (PTR) records to avoid email rejections. As Stoiko Ivanov from Proxmox explains:
The one thing that stands out in that mail-log snippet is that the sending server does not have a PTR entry... enabling: GUI->Configuration->Mail Proxy->Options->Reject Unknown Clients would reject this mail.
For high-traffic environments, invest in enterprise-class SSDs with power loss protection and consider using ZFS for data redundancy. Running a dedicated recursive DNS server on the gateway can help you avoid hitting DNSBL rate limits. To enhance security, ensure your destination mail server is only accessible through the Proxmox Mail Gateway. This prevents spammers from bypassing your filters by connecting directly to port 25. Lastly, restrict access to the web management interface (port 8006) to specific internal IP addresses .
Installation and Configuration of Proxmox Mail Gateway
sbb-itb-bec6a7e
Improving Spam Detection and Email Security
Proxmox Mail Gateway offers a strong foundation for email filtering, but with some adjustments and real-time monitoring, you can enhance security even further.
Fine-Tuning Spam Detection
While Proxmox Mail Gateway's naive Bayesian classifier learns and improves over time, manual training can speed up its accuracy. To train the filter, you'll need around 200 spam and 200 ham messages. Use the sa-learn command to teach it: sa-learn --spam <file> for spam and sa-learn --ham <file> for ham messages. You can also tweak SpamAssassin rule scores by editing the /etc/mail/spamassassin/custom.cf file. After making changes, verify them with spamassassin -D --lint, and restart the pmg-smtp-filter service to apply updates.
DNS configuration plays a big role in detection accuracy. As Stoiko Ivanov from Proxmox explains:
Bad detection rates are often due to a misconfigured DNS setup.
To avoid issues like rate limits from DNSBL providers, consider running a dedicated recursive DNS server on your Proxmox Mail Gateway instance. Additionally, enabling before-queue filtering to reject spam during the SMTP session (using a 554 code) helps reduce server load and prevents backscatter.
These steps help lay the groundwork for better real-time tracking and analysis.
Tracking and Reporting Tools
Proxmox's Message Tracking Center provides a clear, detailed view of each email's journey. It shows everything from arrival and filter results to queue status and final delivery, even in high-volume environments.
For real-time insights, the Real-time Syslog feature displays the last 100 lines of system logs. You can also set up automated daily reports to receive summaries of filtering activity, keeping administrators informed. The Advanced Statistics feature offers deeper insights into email traffic patterns. To focus on active users - those who have sent mail in the last 90 days - enable the advfilter setting.
Security Best Practices
Strong detection tools are essential, but combining them with sound security practices provides even greater protection.
A multi-layered filtering approach is especially effective. By using SPF verification, DNSBL checks, SURBL scanning, and greylisting, Proxmox Mail Gateway can block a wide range of malicious emails. Receiver verification at the SMTP level is another powerful tool. It identifies emails sent to invalid addresses, reducing unnecessary traffic by up to 90%.
For added security, restrict access to the web management interface (port 8006) to specific internal IP addresses or use a VPN for remote access. Regular updates are crucial - use the Proxmox Enterprise Repository to ensure your gateway stays up-to-date with stable and tested security patches.
To improve malware and phishing detection, consider adding unofficial ClamAV signatures from trusted sources. Finally, implementing DKIM signing for outgoing emails can enhance your sender reputation and ensure message integrity.
Conclusion
Proxmox Mail Gateway offers a powerful and budget-friendly solution for spam filtering and email security tailored for open-source platforms. It's especially well-suited for small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs) that rely on open-source email systems, providing a reliable shield against spam, viruses, phishing attempts, and trojans - all while keeping costs manageable.
With receiver verification, email traffic can be reduced by up to 90%, and greylisting further cuts email volume by as much as 50%. Impressively, a single server can handle millions of emails daily across unlimited domains and users. Enterprise support subscriptions are competitively priced, starting at EUR 99 per host annually.
The intuitive web interface makes deployment quick and straightforward, even for those without advanced Linux knowledge. Whether you're using MS Exchange, Postfix, or Lotus Domino, the gateway can be set up between your firewall and internal mail servers in just minutes. Plus, the open-source GNU AGPLv3 license ensures you maintain full control over your email infrastructure without being locked into a specific vendor.
Proxmox Mail Gateway doesn't just stop at simple deployment. It also strengthens your email reputation with robust outbound filtering. Features like outbound filtering and integrated DKIM signing safeguard your sender reputation and ensure the integrity of your emails.
FAQs
How does Receiver Verification in Proxmox Mail Gateway help reduce spam?
Receiver Verification in Proxmox Mail Gateway helps cut down on spam by checking recipient email addresses during the SMTP handshake. If an email is sent to an address that doesn’t exist, it’s rejected on the spot, saving your system from wasting resources.
By blocking these invalid emails early, you can reduce spam and the need for virus scanning by up to 90%, easing the strain on your mail servers and boosting their efficiency.
What are the advantages of using Greylisting in Proxmox Mail Gateway?
Greylisting in Proxmox Mail Gateway is an effective tool for cutting down on spam. It works by temporarily rejecting emails that seem suspicious and requiring the sender to resend them. This simple yet powerful process can block a significant amount of spam - sometimes reducing it by as much as two-thirds - while still allowing legitimate emails to come through after verification.
By tackling spam at an early stage, Greylisting not only keeps your inbox cleaner but also lightens the load on your mail servers. This helps your system run more smoothly and efficiently.
How do I customize spam filtering rules in Proxmox Mail Gateway?
You can fine-tune spam filtering in Proxmox Mail Gateway by adjusting filter rules through the web interface, command-line tools, or SpamAssassin configuration files. If you prefer using the web GUI, head over to Mail Filter → Objects to create a new filter object. Here, you can define its type (like Subject or Header), set a matching pattern, and choose an action such as Reject or Quarantine. Once done, add this object to a filter set under Mail Filter → Filter Sets and save your changes.
For those looking for more advanced options, you can directly edit SpamAssassin rules in the configuration file located at /etc/spamassassin/local.cf. This allows you to define custom patterns and scoring. Don’t forget to restart the filter service after making these changes to ensure they take effect. Additionally, command-line tools like pmgconfig are available for bulk updates or scripting, making it easier to handle complex filtering scenarios.


