Here’s what the research says:
- 78% of workers use AI, but only 14% receive proper training, leading to "shadow AI" risks.
- AI boosts productivity, especially for less-experienced workers (34%-43% gains), but experts only see 17% improvement.
- Studies show 75% of generative AI’s value lies in customer operations, marketing, R&D, and software engineering.
- Proper training can deliver a $4 return for every $1 spent, with measurable results in 12-24 months.
- Employees in AI roles earn an extra $1,470 per quarter, while trained teams achieve faster task completion and higher quality.
Key takeaway: Success depends on job-specific training, leadership support, and tracking ROI over time. Without these, 95% of AI projects fail.
Major Research Findings on AI Training Programs
Harvard Business School Research
In September 2023, Harvard Business School, in collaboration with Wharton and MIT, conducted a study involving 758 Boston Consulting Group consultants (representing 7% of individual contributors) to examine GPT-4's impact on 18 consulting tasks. The research introduced the concept of the "jagged technological frontier" - a term describing how AI excels at certain complex tasks but occasionally struggles with seemingly simple ones.
The results were striking. Consultants using AI completed 12.2% more tasks, worked 25.1% faster, and delivered work of 40% higher quality compared to those without AI assistance. However, when tasks were deliberately designed to challenge AI's current limitations, users relying on AI were 19 percentage points more likely to produce incorrect solutions.
"The capabilities of AI create a 'jagged technological frontier' where some tasks are easily done by AI, while others... are outside the current capability of AI." – Fabrizio Dell'Acqua, Harvard Business School
The study also revealed two distinct approaches to working with AI. "Centaurs" use AI selectively, assigning specific tasks to the system while maintaining a clear division between human and machine work. On the other hand, "Cyborgs" integrate AI deeply into their workflow, treating it as an extension of their own abilities. For SMEs and scale-ups, these insights highlight the importance of identifying tasks that fall within AI's strengths before implementing training programs. This process often begins with running an AI pilot to validate specific use cases.
These findings are not confined to consulting but resonate across various industries.
Industry Productivity Insights
Research across industries shows that AI acts as a "skill leveler", significantly boosting productivity for less experienced workers. Studies reveal that lower-skilled employees see productivity gains between 34% and 43%, compared to a 17% improvement for experts. For SMEs and scale-ups, this means AI can help newer employees quickly gain proficiency, easing the workload on experienced staff and improving overall efficiency compared to manual workflows.
MIT and Wharton Research Results
Additional studies further validate these trends. Between April and November 2023, Stanford, MIT, and Wharton researchers analyzed 5,179 customer support agents at a Fortune 500 software company during a phased introduction of generative AI. The findings showed a 14% increase in issues resolved per hour. Notably, less experienced agents saw their productivity soar by 34%, while seasoned agents experienced little change.
"The AI model disseminates the best practices of more able workers and helps newer workers move down the experience curve." – Erik Brynjolfsson, Director of the Stanford Digital Economy Lab
The benefits extended beyond productivity. The study reported improvements in customer sentiment and employee retention - critical factors for scale-ups aiming for long-term growth. Another field experiment, which concluded in November 2025, involved 7,137 knowledge workers across 66 firms over six months. Workers who incorporated generative AI into their daily tasks saved an average of two hours per week on email management and significantly reduced after-hours work. For SMEs managing high volumes of communication, these time savings translate into increased capacity and provide valuable insights for designing effective training programs.
sbb-itb-bec6a7e
Does AI Actually Boost Developer Productivity? (100k Devs Study) - Yegor Denisov-Blanch, Stanford
Study Metrics Comparison
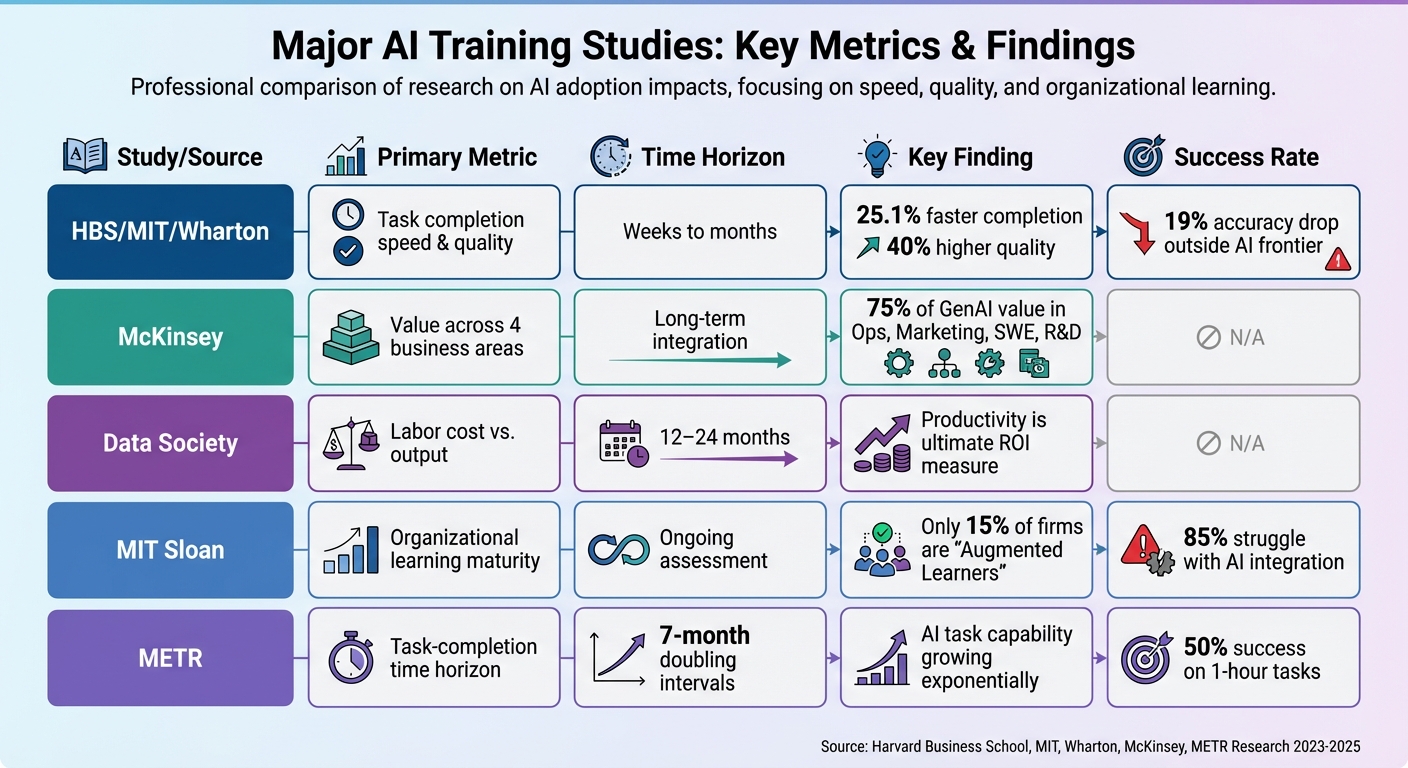
AI Training Research Studies Comparison: Metrics, Timeframes, and Success Rates
Metrics Comparison Table
When comparing major research initiatives, clear differences emerge in how AI training effectiveness is evaluated. Studies from HBS, MIT, and Wharton concentrated on immediate productivity metrics like task completion rates, speed improvements, and output quality. On the other hand, McKinsey's research prioritized long-term value creation across four business areas: customer operations, marketing and sales, software engineering, and R&D. Notably, 75% of generative AI's potential value is concentrated in these areas.
The main distinction lies in the timeframe used for evaluation. HBS/MIT/Wharton studies assessed performance over weeks, while experts like Dmitri Adler, Co-Founder of Data Society, argue that the true return on investment (ROI) for data and AI training programs requires a longer lens: "The return on investment for data and AI training programs is ultimately measured via productivity. You typically need a full year of data to determine effectiveness, and the real ROI can be measured over 12 to 24 months". This extended timeline reveals benefits that shorter studies may miss.
| Study/Source | Primary Metric | Time Horizon | Key Finding | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBS/MIT/Wharton | Task completion speed & quality | Weeks to months | 25.1% faster completion; 40% higher quality | 19% accuracy drop outside AI frontier |
| McKinsey | Value across 4 business areas | Long-term integration | 75% of GenAI value in Ops, Marketing, SWE, R&D | N/A |
| Data Society | Labor cost vs. output | 12–24 months | Productivity is ultimate ROI measure | N/A |
| MIT Sloan | Organizational learning maturity | Ongoing assessment | Only 15% of firms are "Augmented Learners" | 85% struggle with AI integration |
| METR | Task-completion time horizon | 7-month doubling intervals | AI task capability growing exponentially | 50% success on 1-hour tasks |
These metrics highlight how both task duration and organizational readiness shape the success of AI training efforts.
An emerging metric gaining attention is the task-completion time horizon, which measures the duration (in expert hours) that an AI agent can autonomously complete tasks with 50% reliability. Advanced models like Claude 3.7 Sonnet excel at tasks under four minutes, achieving near-perfect success rates. However, for one-hour tasks, success drops to just 50%. Interestingly, this capability has doubled every seven months over the past six years. If this trend continues, AI agents could potentially handle month-long autonomous projects by the end of the decade. This projection underscores both the promise and the challenges organizations will face in adapting to such capabilities.
While productivity gains are a key focus, organizational maturity plays an equally critical role. Only 15% of organizations are classified as "Augmented Learners", meaning they effectively integrate AI into their learning processes. This low adoption rate emphasizes the need for a deeper transformation in how teams learn and adapt. For small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and scale-ups, this isn't just about adopting AI tools - it’s about rethinking workflows and training methods from the ground up.
The gap between expectations and actual outcomes is another factor to consider. For example, a 2025 study revealed that experienced developers anticipated AI would speed up their work by 24%. In reality, they took 19% longer to complete tasks due to additional steps like prompting and reviewing AI-generated outputs. This highlights the importance of managing expectations and addressing inefficiencies in AI integration.
Long-Term Business Outcomes
Efficiency Improvements
Investing in structured AI training is proving to be a financial game-changer. Companies are now seeing a return of nearly $4 for every $1 spent on generative AI initiatives. For instance, a company with $20 billion in revenue could potentially unlock $500 million to $1 billion in additional profits, with about one-third of those profits materializing in just 18 months.
Take DynaChem Research, for example. By implementing custom AI for patent analysis, they eliminated a $7,500 yearly software subscription and cut research time to just one hour, saving an estimated $3,000 in legal fees per patent. Similarly, Staples Technology Solutions saved $40,000 during its initial IT refresh phase by leveraging AI-driven lifecycle solutions.
AI is also transforming project timelines. Tasks that once took two weeks are now completed in as little as five hours. However, the key to achieving these results lies in addressing the "knowledge gap." Studies suggest that 95% of AI initiative failures stem from inadequate training rather than poor tools. Organizations that prioritize proper upskilling can gain a 9- to 12-month competitive edge.
These examples highlight how critical it is to prepare employees effectively. Without the right training, businesses risk losing out on these substantial financial and operational advantages. Small firms can follow an AI integration checklist to ensure they don't miss these critical steps.
Workforce Reskilling Requirements
Despite AI's growing presence in the workplace, a significant training gap persists. While 80% of leaders report regular AI use, frontline adoption lags at just 51%. Even more concerning, only 14% of employees have received formal AI training, increasing the likelihood of unsupervised and potentially risky "shadow AI" usage. This lack of training not only creates security vulnerabilities but also wastes resources on duplicated efforts.
Training doesn’t just save costs - it builds confidence and improves performance. Research shows that at least five hours of training, especially when paired with in-person coaching, significantly enhances AI adoption rates. For example, a global retailer conducted an A/B test across 500 stores and found that trained teams experienced a 150-basis-point sales boost and doubled engagement levels. Workers in AI-exposed roles also see tangible benefits, including an average earnings increase of about $1,470 per quarter after effective retraining.
The right leadership approach makes all the difference. Surveys reveal that 55% of employees feel optimistic about generative AI when strong leadership is in place, compared to just 15% when leadership is lacking. Law Professor Tracy Norton eloquently described this shift:
"I feel like what I was doing before was like writing with crayons on the sidewalk. Now I feel like a rocket scientist".
Still, concerns linger, with 46% of workers worried about job security during AI transitions. Leaders must actively address these fears by emphasizing how AI enhances roles rather than replaces them. Incentives like gamification and digital badges can further ease the transition and encourage participation.
Conclusion: Practical Insights for SMEs and Scale-Ups
The findings are clear: small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) have a notable edge when it comes to integrating AI. In fact, SMEs are three times more likely to succeed than large corporations, largely because they rely on specialized tools rather than attempting complex in-house development.
Achieving success in AI adoption hinges on a few key factors: strong executive support, focused role-based training, and hybrid learning approaches. These programs often combine live sessions, self-paced modules, and hands-on applications over 3–6 week sprints. Leadership plays a pivotal role - initiatives must begin at the C-suite level to ensure a shared vision, sound governance, and clear frameworks for measuring ROI. Additionally, training needs to be tailored to specific job roles to ensure it aligns with the unique demands of each position. These foundational elements help determine the financial investment required to make AI integration effective.
Here’s a breakdown of typical training costs:
- Executive training: $15,000–$50,000
- Manager programs: $8,000–$25,000
- Team training: $3,000–$12,000
Fast-track rollouts, ranging from $20,000–$100,000 over 3–6 months, can often deliver measurable ROI within the first quarter.
To get the best outcomes, businesses should start with thorough needs assessments and use proven methods to evaluate the effectiveness of their training. Establishing internal Centers of Excellence can also provide ongoing mentorship and skill development, which are critical for long-term success. Without sufficient training, companies risk joining the 95% of AI projects that fail.
For SMEs and scale-ups exploring AI tools to complement their training programs, platforms like AI for Businesses offer curated solutions designed to drive business transformation. However, it’s important to remember that technology alone isn’t enough - success depends on pairing the right tools with teams that have the expertise to use them effectively.
FAQs
How does AI training benefit less-experienced workers?
AI training brings several advantages for workers who are newer to their roles, helping them become more productive, pick up skills faster, and meet workplace expectations more effectively. Research indicates that AI tools can improve productivity by about 14%, while also sharpening problem-solving abilities. Generative AI stands out for its ability to speed up learning by sharing insights and best practices from seasoned colleagues, helping new employees reach proficiency more quickly.
There’s also a financial upside to AI-driven training. Employees who undergo AI training have reported an average earnings boost of $1,470 per quarter after retraining. By providing less-experienced workers with cutting-edge tools and knowledge, AI training not only enhances their performance but also increases their overall value to their organizations.
What is the 'jagged technological frontier,' and how does it affect AI performance?
The term 'jagged technological frontier' refers to the uneven pace at which AI technologies are being developed and adopted across various roles, organizations, and tasks. This uneven progress leads to differences in how effectively AI tools can enhance productivity and deliver results.
Take this as an example: certain roles experience significant benefits from AI, such as quicker problem-solving or simplified document creation. On the other hand, some tasks see only modest gains due to challenges like task complexity, how prepared an organization is to adopt AI, or the current limitations of AI itself. This means that AI's impact isn't uniform - it heavily depends on how well these tools are integrated into specific work settings.
For businesses to thrive in this unpredictable landscape, it's crucial to thoughtfully implement and tailor AI solutions to meet the unique needs of different tasks and teams.
Why do most AI projects fail without proper training?
Most AI projects fall short without adequate training, mainly because businesses often don’t have the know-how to implement and manage AI systems effectively. This can result in issues like clunky integration with current workflows, AI tools being underused, and missing out on the real benefits these systems can offer.
With the right training, teams can learn how to use AI tools efficiently, align them with their business objectives, and adjust as the demands of AI-driven solutions evolve. Without this critical groundwork, it’s tough for organizations to see real returns on their AI investments.