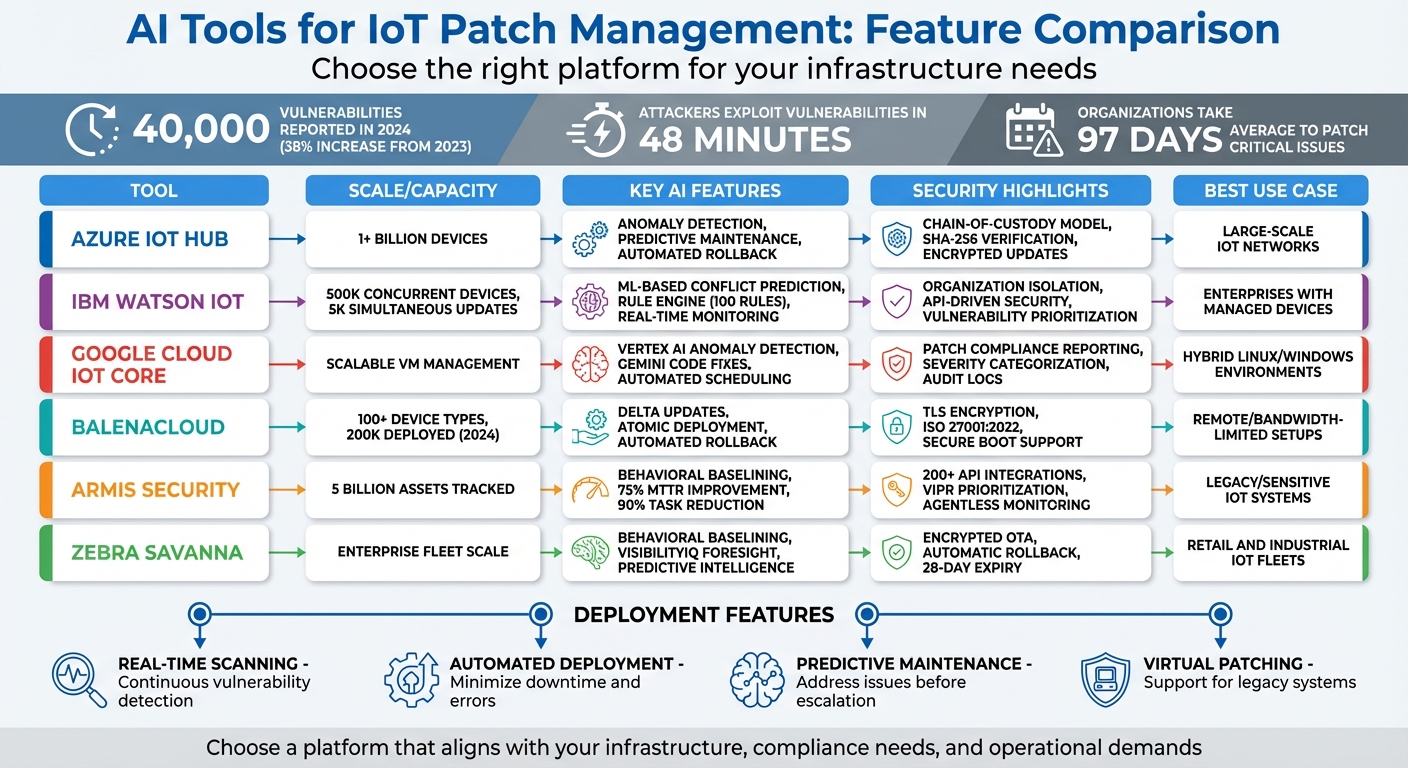
Keeping IoT devices secure and up-to-date is a major challenge. Many devices lack the capacity for seamless updates, often requiring downtime. With 40,000 vulnerabilities reported in 2024 (a 38% increase from 2023), patch delays leave systems exposed to threats. Attackers can exploit vulnerabilities in as little as 48 minutes, while organizations take an average of 97 days to patch critical issues.
AI-driven tools solve this by automating patch management, identifying vulnerabilities, and prioritizing updates. Key benefits include:
- Real-time scanning to detect issues across vast IoT networks.
- Automated patch deployment to minimize downtime and errors.
- Predictive maintenance to address potential issues before they escalate.
- Virtual patching for legacy systems unable to receive updates.
Top AI Tools for IoT Patch Management:
- Azure IoT Hub: Automates updates for over a billion devices with rollback features and strong security protocols.
- IBM Watson IoT Platform: Uses machine learning to predict patch conflicts and streamline updates for up to 500,000 devices.
- Google Cloud IoT Core: Integrates with Vertex AI for anomaly detection and offers flexible patch scheduling.
- BalenaCloud: Focuses on container-based updates, reducing bandwidth and supporting over 100 device types.
- Armis Security: Provides agentless monitoring and risk prioritization, ideal for legacy and sensitive environments.
- Zebra Savanna: Offers OTA updates with behavioral monitoring and automated rollback for failed patches.
Quick Comparison
| Tool | Key Features | Security Focus | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Azure IoT Hub | Automated updates, rollback, real-time monitoring | Firmware integrity, encrypted updates | Large-scale IoT networks |
| IBM Watson IoT | Predictive maintenance, rule-based updates | Risk prioritization, secure APIs | Enterprises with managed devices |
| Google Cloud IoT | Vertex AI, patch scheduling, compliance | Patch compliance, detailed logging | Hybrid Linux/Windows environments |
| BalenaCloud | Delta updates, container-based orchestration | TLS encryption, ISO 27001 certified | Remote or bandwidth-limited setups |
| Armis Security | Agentless monitoring, anomaly detection | Risk prioritization, early warnings | Legacy or sensitive IoT systems |
| Zebra Savanna | OTA updates, behavioral baselining | Encrypted OTA, rollback mechanisms | Retail and industrial IoT fleets |
AI tools provide faster, smarter ways to manage IoT patches, reducing downtime and improving security. Choose a platform that aligns with your infrastructure and operational needs.
AI-Powered IoT Patch Management Tools Comparison Chart
Mitigate IoT/OT Vulnerabilities With Guided Virtual Patching (Sponsored)
1. Azure IoT Hub with AI-Powered Patch Management
Azure Device Update for IoT Hub simplifies over-the-air (OTA) updates for everything from sensors to gateways. With support for over a billion IoT devices worldwide, it’s a go-to solution for managing firmware updates on a massive scale.
Anomaly Detection & Predictive Maintenance
The platform leverages AI to monitor IoT data in real time, spotting trends and patterns that could indicate potential issues before they become critical. If a failure occurs, it pinpoints the affected device and provides detailed error data, saving time spent on manual troubleshooting. By analyzing equipment performance data, the system forecasts maintenance needs, helping businesses avoid costly breakdowns and unplanned downtime.
Automation in Patch Deployment
Azure IoT Hub streamlines the entire update lifecycle using device twin properties, automating processes like downloading, installing, and applying updates. Devices are grouped based on compatibility, enabling precise, scalable rollouts. If an update fails, the system automatically rolls back to a predefined fallback version, ensuring devices remain functional. Gradual rollouts, starting with test groups, reduce the risk of widespread issues during production deployments. This level of automation integrates smoothly with existing enterprise workflows.
Integration with Existing Enterprise Systems
The service is deeply integrated with Azure IoT Hub and supports IoT Plug and Play interfaces. With programmatic APIs and Azure CLI, teams can automate tasks and create custom portals, embedding update workflows into their CI/CD pipelines. For setups with limited connectivity, features like nested edge and on-premises content caching ensure updates reach offline devices. Compliance checks can be scheduled every 24 hours to ensure devices stay up-to-date.
Security Features for Firmware Updates
Azure employs a chain-of-custody model to ensure updates are trusted, unaltered, and authorized. Devices validate updates using root keys embedded in the Device Update agent. Microsoft issues signing key pairs, and the agent verifies the signing key against the root key before confirming the update manifest’s signature. The manifest includes file hashes (SHA-256) that the agent cross-checks with downloaded binaries to confirm integrity. Updates are encrypted while stored in Azure Storage and transmitted securely over IoT Hub channels. Microsoft also rotates signing keys frequently, and devices running agent version 1.1.0 or later automatically download new root key packages.
2. IBM Watson IoT Platform
IBM Watson IoT Platform takes an integrated approach to simplify and secure firmware updates, building on the principles of AI-driven patch management.
The platform operates on a managed device architecture. This means only devices equipped with a management agent can perform automated firmware downloads and updates. Under the Lite plan, it supports up to 500,000 concurrent devices and allows one management action to be applied across 5,000 devices at a time.
Anomaly Detection & Predictive Maintenance Capabilities
IBM Watson IoT Platform processes IoT data in real time to identify trends and detect irregularities that could indicate patch issues. By leveraging machine learning models, it uses historical deployment and usage data to predict potential patch conflicts. After updates are deployed, AI continues to monitor devices, identifying anomalies or suspicious behavior that might suggest a failed update or even a security breach. Additionally, the platform evaluates performance data to predict when patches or firmware updates are needed, helping to prevent equipment failures, reduce downtime, and avoid costly disruptions.
Automation Level in Patch Deployment
The platform uses the Device Management Protocol to remotely execute tasks like restarts, factory resets, and firmware updates. These actions are automated through API keys and unique application IDs, streamlining patch workflows. AI systems prioritize patches based on their risk level and business impact, determining the order of updates automatically. A rule engine, supporting up to 100 rules per organization, triggers patching workflows whenever specific conditions are met. This allows businesses to respond swiftly to vulnerabilities.
Integration with Existing Enterprise Systems
IBM Watson IoT Platform facilitates seamless communication between devices and the cloud using MQTT and HTTP protocols. It can integrate with up to 12 external services and works alongside Maximo Asset Monitor for better asset health tracking. For messaging, device-to-cloud persistence lasts 24 hours, while cloud-to-device persistence defaults to 48 hours. The Lite plan also sets API call limits at 10 calls per second, with a maximum message size of 128 KB.
Security Features for Firmware Updates
To ensure secure operations, the platform uses six-character "Organization" identifiers, which isolate management commands and data, making them accessible only to authorized devices and applications. Direct communication between different organizations is restricted. IBM’s AI-driven vulnerability management further enhances security by providing prioritized recommendations. This helps businesses focus on critical risks and significantly reduces the time required to address security patches, ensuring a faster response to emerging threats.
3. Google Cloud IoT Core with AI Integration
Google Cloud IoT Core leverages Vertex AI to identify anomalies in device behavior, such as input skew and drift, before they cause larger issues. The platform's Gemini models add another layer of functionality by automating the creation of code fixes for vulnerabilities uncovered during unit tests. Together, these features streamline the patching process, making it faster and more efficient.
Automation Level in Patch Deployment
Google Cloud's VM Manager, part of the OS Config service, simplifies patch deployment for large-scale Linux and Windows environments. It allows for scheduling of one-time or recurring patch jobs - whether weekly, monthly, or on specific days - using instance filters to target devices based on name, zone, or labels. Advanced rollout controls, such as zone-specific deployments and concurrent updates, ensure flexibility, while a disruption budget limits the number of devices taken offline simultaneously.
Administrators can also configure pre- and post-patch scripts for tasks like shutting down applications or conducting health checks. The OS Config agent updates inventory data every 10 minutes, and patch job details are accessible within 30 minutes.
"The service makes patching Linux and Windows VMs with the latest OS upgrades simple, scalable and effective." - Dmitry Sadakov, Software Engineer, Google Cloud
Integration with Existing Enterprise Systems
Beyond automation, Google Cloud IoT Core integrates seamlessly with enterprise workflows to ensure smooth operations.
Through the VM Manager API (OS Config API), CI/CD pipelines can trigger patch jobs using RESTful POST requests or the Google Cloud CLI (gcloud). Instance filters enable dynamic targeting of devices based on labels like env=prod or app=gateway, eliminating the need to modify deployment schedules. Pre-patch and post-patch scripts stored in versioned Cloud Storage buckets ensure only approved scripts are executed during updates. Additionally, the OS Config agent offers real-time compliance updates on a centralized dashboard, cross-referenced with vulnerability sources for added security.
Security Features for Firmware Updates
Google Cloud ensures robust security for firmware updates through data access audit logs, which track every patch management event for compliance purposes. Patch compliance reporting categorizes updates by severity - Critical (RED), Important/Security (ORANGE), Other (YELLOW), or Up-to-date (GREEN) - based on inventory data and OS package metadata. Maintenance windows can also be set to restrict automated patching to specific times, reducing the risk of disruptions during critical business hours.
sbb-itb-bec6a7e
4. BalenaCloud with AI-Driven Update Orchestration
BalenaCloud takes a container-based approach to IoT patch management, which helps streamline updates across devices. By generating binary deltas - essentially just the differences between container images - it minimizes bandwidth usage and downtime. This is especially beneficial for managing devices in remote areas with limited connectivity. These optimizations set the stage for efficient and reliable automation in deploying patches.
Automation Level in Patch Deployment
BalenaCloud's update process is atomic, meaning updates either fully succeed or the system reverts to its previous working state without altering boot settings to the new partition. If an update fails, automated rollback is triggered through health checks or by detecting an unbootable system. The platform's on-demand delta generation ensures even older software versions can be updated without unnecessary overhead.
In 2024, Seeed Studio successfully deployed 200,000 LoRaWAN devices in just one year, leveraging BalenaCloud's automated provisioning and update orchestration. The platform supports more than 100 device types, including Raspberry Pi, NVIDIA Jetson, and x86 architectures. Developers also benefit from access to over 26,000 IoT-focused base images, which significantly speed up development.
"Being able to do software related tasks remotely, and managing and deploying to a large installed base are definitely the killer features of balena." - Stefan Rauch, Software Engineer, Bosch
Integration with Existing Enterprise Systems
BalenaCloud integrates seamlessly with enterprise workflows. Its CLI and API allow direct connections to CI/CD pipelines, enabling automated builds and deployments. Developers can push updates remotely using commands like "git push" or "balena push", which trigger image builds and fleet-wide updates. Additionally, the platform exports device logs and health metrics to external monitoring tools such as InfluxDB and Grafana through its API.
For environments without internet access, the "preload" process simplifies provisioning. It flashes the OS and the latest application release onto devices in a single step, making it easier to deploy devices in air-gapped settings.
"The API is quite powerful and helps us automate quite a bit of our work. There's no service we're aware of that's comparable." - Flavia Paganelli, Co-founder and Director of Engineering, 30MHz
This integration aligns with BalenaCloud's strong focus on security during firmware updates.
Security Features for Firmware Updates
BalenaCloud ensures secure communication between devices and its service by using HTTPS with TLS encryption for all interactions, including Docker image downloads and pull requests. Its Information Security Management System is certified under ISO 27001:2022, guaranteeing structured security protocols. Each device is provisioned with a unique API key, allowing administrators to revoke compromised keys without disrupting the rest of the fleet.
For x86_64 hardware, the platform supports Secure Boot and Full Disk Encryption, enhancing device integrity. Additionally, it provides SBOM (Software Bill of Materials) tracking, which helps organizations meet regulatory requirements like the EU's Cyber Resilience Act.
5. Armis Security for IoT Vulnerability Detection
Armis Security focuses on providing visibility and prioritizing risks rather than directly deploying patches. Its agentless monitoring system tracks over 5 billion assets globally through the Asset Intelligence Engine, a cloud-based AI knowledge base that establishes behavioral baselines for various device types.
Anomaly Detection and Predictive Maintenance Capabilities
Armis uses machine learning to monitor device behavior in real time, spotting deviations that could signal misconfigurations or security threats. By tailoring behavioral profiles to each device, it minimizes false positives through contextual analysis.
In Jonesboro, Arkansas, Jason Ratliff, Director of Information Systems, shared how Armis transformed their approach to securing critical infrastructure. The platform uncovered 30% more devices than they initially knew about, significantly enhancing their security efforts. Similarly, a European water utility serving 5 million people adopted Armis Centrix™ to secure thousands of water treatment plants from 31 operators, ensuring compliance with EU regulations.
"Armis gave us the complete visibility we needed across both IT and OT environments. We discovered 30% more devices than we thought we had, which has transformed how we secure our city's critical infrastructure." - Jason Ratliff, Director of Information Systems, Jonesboro Arkansas
Organizations using Armis Centrix™ for VIPR Pro have seen a 75% improvement in Mean Time to Remediate (MTTR). The platform's AI module provides early warnings about vulnerabilities that attackers are exploiting, often months ahead of public disclosure. Additionally, AI-driven automation has reduced operational tasks like manual ticketing by up to 90%.
These capabilities allow seamless integration with enterprise systems, enabling real-time enforcement of security measures.
Integration with Existing Enterprise Systems
Armis Centrix supports over 200 pre-built API integrations with popular tools like ServiceNow, Jira, BMC, SIEM platforms, and firewalls. Its open API framework also allows custom integrations for CI/CD pipelines and specialized telemetry systems. When anomalies are detected, the platform can automatically trigger actions such as quarantining devices through Network Access Control (NAC) or blocking malicious traffic via firewalls.
Armis consolidates alerts from various vulnerability scanners, including Qualys and Tenable, into a single prioritized view. This automation reduces time spent on manual alert assessments by 80%, streamlining the process from detection to resolution. Such integration highlights how AI can simplify IoT patch management, enabling rapid responses to vulnerabilities.
Security Features for Firmware Updates
While Armis doesn’t directly deploy patches, its security analytics strengthen firmware management by verifying compliance and identifying vulnerable configurations. The platform compares firmware and software versions against a global database of "known-good" baselines, flagging outdated or vulnerable versions. It also tracks encryption compliance, helping organizations pinpoint non-compliant devices.
Armis’s VIPR (Vulnerability Intelligence and Prioritization) system goes beyond standard CVSS scores by ranking vulnerabilities based on business importance, exploitability, and active threat intelligence. With access to a database profiling over 6 billion assets, Armis Labs delivers early warnings for critical vulnerabilities, sometimes up to 46 days before public disclosure.
"Armis provides us with real-time visibility and control over our assets, allowing us to proactively manage security risks and improve our operational efficiency." - CISO, Medical Device Company
This approach is particularly valuable for legacy IoT and OT devices that can’t support traditional security agents. By using passive monitoring, Armis avoids disruptions, making it ideal for sensitive environments like industrial or medical IoT, where active scanning could lead to system crashes or downtime.
6. Zebra Savanna: AI-Powered IoT Device Management
Zebra Savanna brings together real-time edge data to fuel VisibilityIQ Foresight, offering actionable insights into device health and performance. This system supports LifeGuard OTA (Over-the-Air), a service designed to roll out firmware security updates across entire device fleets.
Anomaly Detection and Predictive Maintenance Capabilities
Zebra Savanna’s AI shifts from traditional threat detection to behavioral baselining, spotting subtle changes that could indicate maintenance needs or vulnerabilities. By understanding the "personality" of the IoT network, it identifies issues or unusual activity that signature-based methods often miss.
With VisibilityIQ, organizations gain clear insights into device health, usage, and support, enabling smarter fleet management. The platform uses predictive intelligence to highlight specific assets - like those with a vulnerable chipset - allowing for prioritized and automated patching. This transition from reactive to proactive security relies on establishing "normal" behavioral patterns for unmanaged IoT devices.
These tools make patch deployment more efficient and targeted.
Automation Level in Patch Deployment
Zebra Savanna simplifies update processes with two LifeGuard OTA modes: Full Automation (updates are applied automatically within 1-3 days over any network) and Flexible Automation (administrators set rules through EMM).
The system uses a BuildID to compare the device’s current OS version with the latest release, ensuring patches are applied accurately. Updates follow a cumulative model - each one includes fixes from all previous versions. Additionally, LifeGuard OTA services are offered free of charge to EMM partners.
Security Features for Firmware Updates
Zebra ensures secure firmware and patch delivery through its Common Transport Layer (CTL). Accessing LifeGuard OTA’s API requires both a Zebra application key and valid authorization tokens. For Android 11 and later, Zebra includes an automatic rollback feature: if an update fails to boot, the device reverts to its last working OS image.
Devices must first be enrolled via the Zebra Enrollment Manager to receive secure OS updates. Update packages are sent as delta packages, which only include the changes necessary for the update, saving bandwidth and storage space. To avoid outdated patches being installed, LifeGuard OTA upgrade requests automatically expire after 28 days.
Conclusion
In 2024 alone, over 40,000 vulnerabilities were published, and attackers demonstrated the ability to move laterally through networks in just 48 minutes. This highlights a critical gap between the emergence of threats and their remediation. Traditional patching methods, which take 77% of organizations a week or more to implement, leave systems dangerously exposed during this window.
Modern solutions offer a smarter approach. Automated vulnerability identification provides real-time scanning of devices and manufacturer repositories, while intelligent prioritization focuses resources on the most pressing risks based on actual exploitability. Machine learning-driven compatibility analysis predicts potential deployment issues before they arise. These advancements turn patch management into a proactive security measure rather than a reactive challenge. As Gartner analysts Tom Cipolla and Dan Wilson observed, "AEM represents the most significant advancement in endpoint management in over a decade". Such insights are invaluable when deciding on the right tools for your organization.
When exploring these AI-driven tools, ensure they meet specific business needs. Look for features like rollback capabilities and legacy compatibility testing tailored to your hardware mix. Confirm that the platform actively monitors a wide range of manufacturer repositories, even capturing updates where version numbers remain unchanged. In high-stakes environments, human oversight remains crucial to account for unique factors like regulatory requirements or business priorities.
The evolution toward autonomous systems that identify, prioritize, and remediate vulnerabilities without constant human input is more than just a time-saver - it's essential. With 98% of IT professionals reporting that manual patching disrupts critical business operations, this shift ensures organizations can close exposure gaps before attackers exploit them. To stay ahead, choose tools that align with your infrastructure, compliance needs, and operational demands. This proactive approach not only strengthens security but also safeguards business continuity in an increasingly hostile digital landscape.
FAQs
How can AI tools make IoT patch management faster and more efficient?
AI tools simplify IoT patch management by automating essential tasks, cutting down on manual work, and reducing the chance of mistakes. They can scan extensive IoT networks to spot vulnerabilities, rank risks based on their urgency, and apply patches remotely - all without needing hands-on intervention or causing device downtime.
Using advanced algorithms, these tools pair vulnerabilities with the appropriate patches, ensuring critical updates are rolled out quickly. By handling large-scale patch deployments automatically, they keep devices secure and running smoothly with minimal interruptions. This method enables organizations to address threats quickly and manage updates effectively, saving both time and resources in the process.
What security features do AI-powered IoT patch management tools offer?
AI-powered IoT patch management tools come equipped with strong security measures to ensure updates for connected devices are both safe and reliable. For instance, these tools use digital signatures to verify the source and integrity of patches, ensuring updates are from trusted providers and haven't been altered.
They also offer automated vulnerability detection and prioritization, allowing organizations to quickly identify and address the most critical security gaps. This reduces the risk of potential breaches. On top of that, features like role-based access controls and credential management add another layer of protection, preventing unauthorized changes during the patching process and shielding devices from internal or external threats. Together, these capabilities help secure IoT networks while keeping them running smoothly.
How can AI tools improve security for legacy IoT devices that can't be updated?
AI tools play a vital role in improving the security of older IoT devices through virtual patching. This technique safeguards devices from known vulnerabilities by applying security measures at the network level. Instead of relying on traditional updates, virtual patching blocks harmful traffic, keeping devices secure while allowing them to operate without disruptions.
On top of that, AI-driven solutions can handle tasks like spotting vulnerabilities, evaluating risks, and responding to threats automatically. These tools help prioritize potential dangers, simplify firmware updates, and cut down on manual work, leading to quicker and more effective protection. For legacy devices that no longer receive vendor updates, AI offers a proactive way to defend against threats while keeping the devices running smoothly.